Still building LLM apps and stuck on RAG vs fine tuning, while your AI continues to miss context or return outdated answers? You’re not alone. Many teams struggle to get accurate, reliable outputs from their AI automation. Growth Design Studio designs custom LLM systems that solve these issues—so your AI delivers real, measurable business outcomes.
This post will walk you through two powerful strategies—Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) and Fine-Tuning—showing you how each works, when to use them, and how to pick the best fit for your AI automation needs. By the end, you’ll know exactly how to get your LLM apps producing reliable, on-point information every time.
Why Accuracy and Context Matter in Automation
When you automate tasks with AI, the quality of the output directly impacts your business. Flawed information from an LLM can quickly derail a workflow. At Growth Design Studio, we prioritize designing automation frameworks for reliability and performance, understanding that precise outputs are critical for your operations.
The Cost of Wrong Outputs
Imagine an automated customer service bot giving incorrect product details or a sales agent generating a proposal with outdated pricing. These errors waste time and money. They can also damage customer trust. Getting it right the first time is crucial for efficient AI automation.
Our solutions, including AI voice agents and sales automation, are engineered to minimize such errors, ensuring your automated processes build trust and drive revenue, not rework. For more on automated customer support strategies, see our guide on automated customer support benefits.
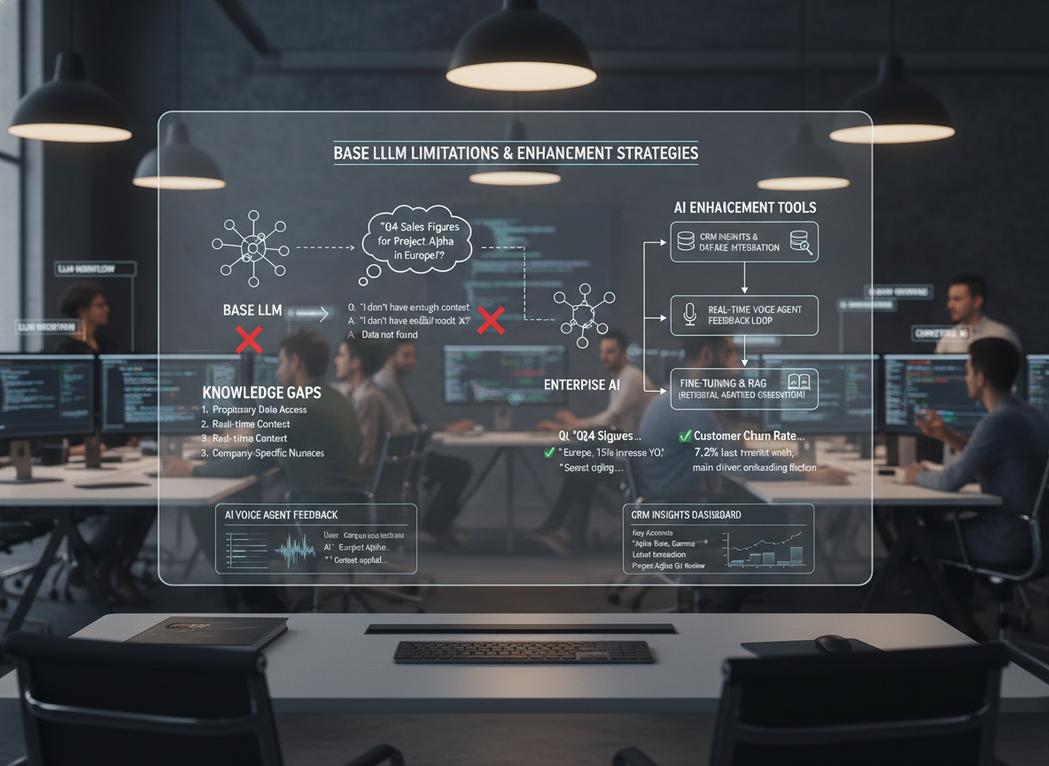
Why “Base Models” Aren’t Enough
General-purpose Large Language Models (LLMs) are powerful, but they’re trained on vast, general internet data. They don’t inherently know your company’s specific policies, product catalog, or internal documents.
Relying on a base model for specialized tasks often leads to generic or hallucinated responses. This is where methods like RAG and fine-tuning come in. Growth Design Studio helps small and mid-sized businesses overcome these limitations by implementing tailored AI strategies that leverage your unique data and processes.
What Is Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)?
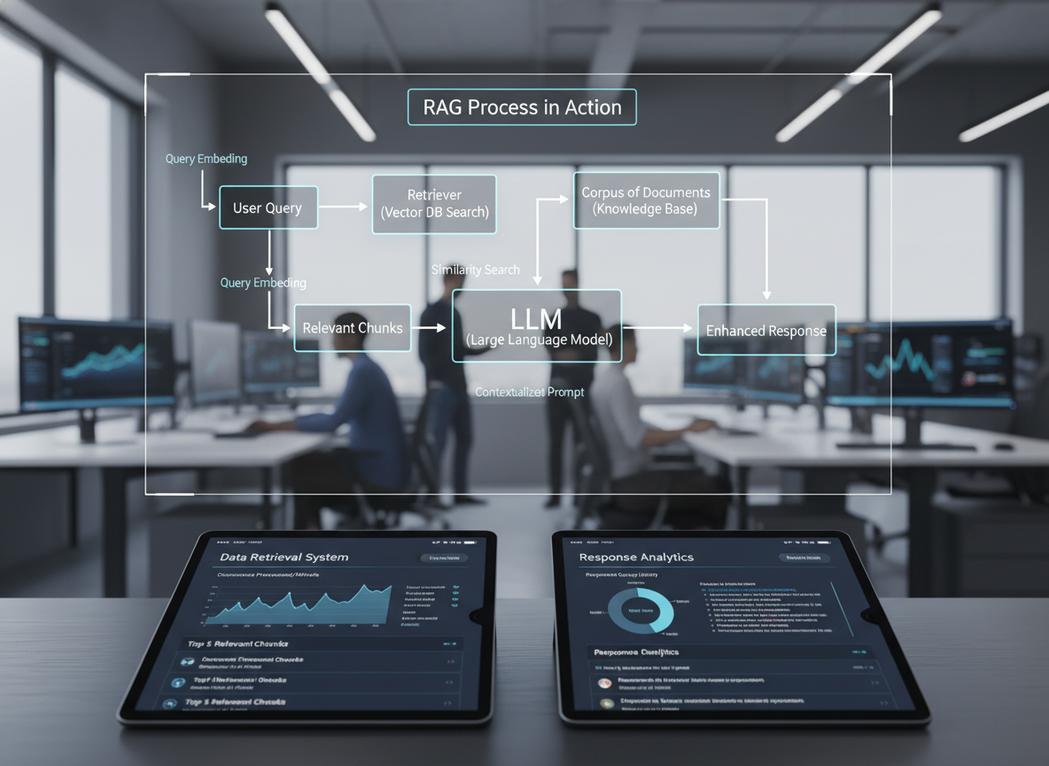

RAG is like giving your LLM a focused “brain” by connecting it to an external knowledge base. When the LLM gets a query, it first retrieves relevant information from your specific data sources, then generates a response based on that retrieved context.
How RAG Works
Think of RAG as a smart librarian. When you ask a question, the librarian (the retrieval component) quickly finds the most relevant books or documents from your library (your data). Then, they use that specific information to answer your question. The LLM acts as the answer generator, synthesizing information from the retrieved documents. This helps build LLM apps that are highly contextual. Growth Design Studio frequently implements RAG systems for clients to ensure their LLM applications provide precise, up-to-date information directly from their internal knowledge bases, powering effective customer support and internal tools. Learn more about building LLM apps in our beginner’s guide to AI automation.
Components of a RAG System
A typical RAG setup includes:
- Vector Database: Stores your company’s documents, converted into numerical representations (embeddings) for fast, semantic search.
- Retriever: Searches the vector database for the most relevant information given a user’s query.
- LLM: Takes the retrieved information and the original query, then generates a coherent, context-aware answer.
This allows for real-time access to the latest data without retraining the core model. Our expertise in workflow orchestration using tools like n8n and custom API integrations enables us to seamlessly connect these RAG components, delivering robust and scalable solutions.
What Is Fine-Tuning in LLMs?

Fine-tuning involves taking a pre-trained LLM and further training it on a smaller, specific dataset. This process adjusts the model’s internal weights, making it better at understanding specific patterns, tones, or tasks relevant to your data.
How Fine-Tuning Changes Model Behaviour
Instead of simply looking up information, fine-tuning teaches the model to think differently. It adapts the LLM’s language style, factual understanding, or even its ability to follow specific instructions. For example, you can fine-tune an LLM to generate code in a specific programming language or write marketing copy in your brand’s voice.
Types of Fine-Tuning (SFT, LoRA, Adapters)
There are several ways to fine-tune an LLM:
- Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT): This is the most common method, using labeled examples to teach the model desired inputs and outputs.
- LoRA (Low-Rank Adaptation): A more efficient method that only trains a small number of new parameters, making it faster and cheaper than full SFT.
- Adapters: These are small neural network modules inserted into the LLM, trained on specific tasks without changing the original model’s weights.
When selecting your LLM for fine-tuning, consider options like OpenAI vs open-source models, as detailed in our post on choosing the right LLM for AI automation.
RAG vs Fine Tuning: Key Differences
Choosing between RAG and fine tuning depends on what you need your LLM automation to do. Both have unique strengths.
Accuracy and Freshness of Information
- RAG: Excels at providing highly accurate and current information. Since it retrieves directly from your live data, updates are instantly reflected in responses. This is perfect for dynamic knowledge bases.
- Fine-Tuning: Improves the model’s general understanding and output style based on the training data. However, if that data becomes outdated, the fine-tuned model’s knowledge will also be outdated until retrained.
Cost and Time to Implement
- RAG: Generally quicker to implement for information retrieval tasks. You mainly need to set up your vector database and integrate it with an LLM. This makes it a great choice for AI automation with existing knowledge bases. Growth Design Studio’s fast implementation approach means businesses can quickly deploy RAG solutions to leverage their existing data for immediate gains in efficiency. Explore how RAG fits into broader workflows in our comparison of AI automation vs traditional automation.
- Fine-Tuning: Requires preparing a high-quality dataset and significant computational resources for training. It’s a more involved process and often takes longer to achieve the desired results.
Maintainability and Updates
- RAG: Easy to update. Simply add or remove documents from your knowledge base, and the system reflects changes immediately.
- Fine-Tuning: More complex to maintain. Each time your knowledge changes significantly, you may need to re-fine-tune the model, which can be costly and time-consuming.
Risk of Overfitting
- RAG: Low risk of overfitting the LLM itself, as the model acts as a retriever and generator rather than a pure memorizer of specific facts.
- Fine-Tuning: Higher risk of overfitting. If your training dataset is too small or not diverse enough, the model might only perform well on that specific data, failing on new or slightly different inputs.
Which Approach Is Better for Automation Use Cases?
Your specific automation goal should guide your choice. Growth Design Studio works closely with small and mid-sized businesses across real estate, healthcare, professional services, and local services to identify the optimal LLM strategy that aligns with their unique objectives.
Knowledge-Based Automation
If your goal is to provide accurate answers from a specific set of documents (e.g., internal policies, product manuals, customer FAQs), RAG is usually the better choice. It ensures the LLM always references the latest, most authoritative information without needing constant retraining.
For scenarios like enhancing customer support or streamlining internal inquiries, Growth Design Studio leverages RAG to build highly effective and data-driven AI agents.
Process and Behaviour Automation
When you need the LLM to learn a specific writing style, follow complex instructions, or perform tasks requiring nuanced understanding not present in a base model (e.g., generating highly specific marketing copy, coding snippets, or summarizing documents in a particular format), fine-tuning shines. It changes the model’s core behavior.
Our expertise in custom API integrations and workflow orchestration using platforms like n8n allows us to implement fine-tuned models for specialized tasks, ensuring the AI behaves exactly as your business requires.
Regulatory and Compliance Scenarios
For industries with strict regulatory requirements, RAG can be advantageous. You can audit the sources the LLM used to generate its response, making it easier to verify accuracy and compliance. Fine-tuning offers less direct traceability to specific source documents.
Hybrid Approaches: Using RAG and Fine-Tuning Together
Sometimes, the best solution combines both methods, leveraging their strengths. Growth Design Studio often designs hybrid systems to give our clients the best of both worlds, ensuring both precise knowledge retrieval and tailored AI behavior.
When Hybrid Systems Make Sense
A hybrid approach is powerful when you need both specialized knowledge and customized behavior. For example, you might fine-tune an LLM to understand your brand’s tone, then use RAG to ensure it pulls accurate, up-to-date product information from your database. This helps you build LLM apps that are both informed and on-brand.
Our problem-first approach ensures that these hybrid architectures are designed to tackle your specific business challenges, leading to highly effective and impactful AI automation.
Architecture Overview
In a hybrid setup, the fine-tuned LLM still processes the query. However, before generating the final answer, it might trigger a RAG process to fetch specific facts from an external knowledge base. The fine-tuned model then uses its improved understanding and the retrieved context to formulate a response.
Decision Framework for Teams
Making the right choice involves looking at your project’s practical aspects. Growth Design Studio guides clients through this decision-making process, providing practical automation design and focusing on real business outcomes over technological hype.
Data Availability
- Abundant, constantly updated documents? RAG is a strong contender.
- Specific, high-quality examples of desired outputs (e.g., 1,000 examples of customer service responses)? Fine-tuning might be appropriate.
Change Frequency
- Information changes often? RAG is easier to keep current.
- Core task/behavior is stable? Fine-tuning can set a consistent foundation.
Budget and Scale
Fine-tuning can be more expensive and resource-intensive, especially for large models or frequent retraining. RAG often offers a more cost-effective way to introduce domain-specific knowledge. Consider your long-term operational costs for AI automation. Growth Design Studio designs scalable automation solutions with a focus on ROI, helping businesses achieve efficiency without excessive overhead.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main difference between RAG and fine-tuning?
RAG retrieves external data for context in real-time, ideal for up-to-date info, while fine-tuning adapts the model’s core behavior through training on specific data, best for custom styles or tasks.
When should I use a hybrid RAG and fine-tuning approach?
Use hybrids when you need both factual accuracy from live data (RAG) and tailored outputs like brand voice or instructions (fine-tuning), such as in customer support or content generation.
Is RAG cheaper than fine-tuning for LLM automation?
Yes, RAG is often more cost-effective as it avoids retraining; it just requires a vector database setup. Fine-tuning needs compute resources and data preparation.
Can fine-tuning lead to outdated information in AI apps?
Yes, if the training data ages. RAG keeps responses fresh by pulling from current sources, making it better for dynamic environments.
How does Growth Design Studio help with RAG or fine-tuning implementation?
We assess your needs, build custom solutions with tools like n8n, and ensure scalable AI automation. Book a free audit to get started.
Conclusion
Choosing between RAG and fine-tuning isn’t about finding a single “best” solution, but rather the right solution for your specific AI automation challenge. RAG excels at giving your LLM current, factual knowledge, while fine-tuning teaches it new skills or a specific voice. Often, combining both gives you the most powerful, flexible, and accurate LLM applications. Your goal is to streamline tasks and save time, and picking the right strategy gets you there faster.
Growth Design Studio helps small and mid-sized businesses navigate these choices, providing tailored automation solutions that significantly reduce manual work and accelerate growth.
Want this automation done for you? Book your free automation audit to see how Growth Design Studio helps teams choose and implement the right LLM strategy.








