What are AI Agents?
AI agents are autonomous software systems that use artificial intelligence to pursue goals, make decisions, and complete tasks on behalf of a user or business without constant human input. They combine techniques like machine learning, natural language processing (NLP), and data reasoning to act intelligently in dynamic environments.
What makes an AI system an “agent”
An AI system is considered an agent when it demonstrates autonomy — that is, when it independently perceives its environment, reasons about what it observes, and acts to achieve objectives set by humans or the business. True AI agents also show planning, learning, and adaptive behavior rather than executing pre-set, static instructions.
How AI agents observe, decide, and act
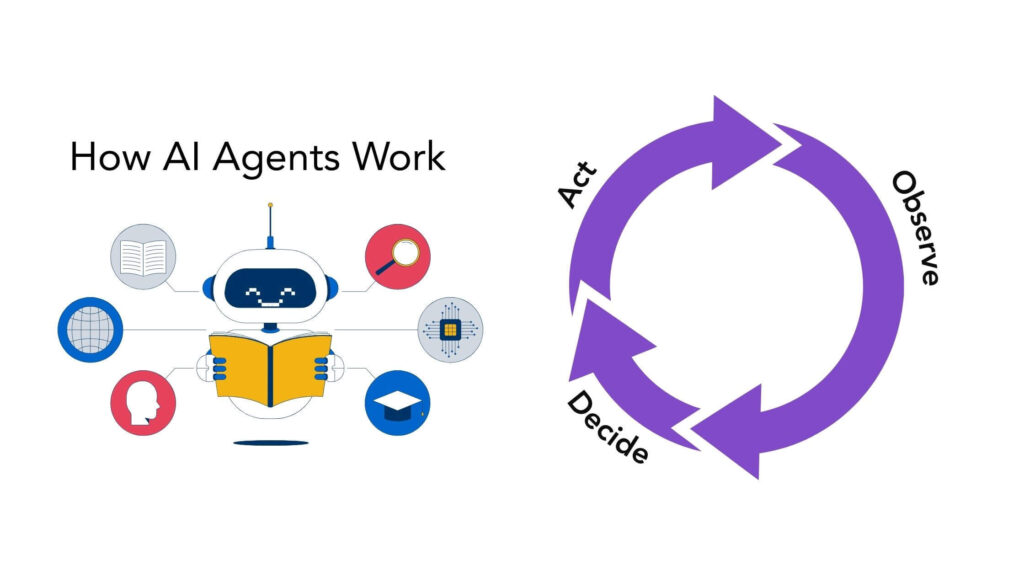
AI agents operate in a continuous loop:
- Observe data or environment – Agents collect inputs from systems or users.
- Decide – They process inputs using AI models and rules, deciding on the next steps.
- Act – They carry out actions such as generating responses, triggering other tools, or updating records.
This observe → decide → act cycle enables agents to respond dynamically and adjust behavior over time.
Must Read: How AI Agents Work: A Practical Guide to Autonomous LLM Automation
Type of AI Agents
AI agents come in various forms depending on complexity and purpose. Common categories include:
- Simple reflex agents — react immediately to inputs.
- Goal-based agents — decide actions based on specific objectives.
- Utility-based agents — choose actions to maximize measured “utility.”
- Learning agents — improve their decisions using feedback.
- Multi-agent systems — several agents coordinate on shared tasks.
How do they differ from Traditional workflows?
AI agents fundamentally differ from standard workflows by how decisions are made and actions are taken.
AI agents vs rule-based automation
Traditional automation runs exactly as it was programmed — rigid sequences triggered by specific inputs. It cannot adapt beyond its fixed rules.
By contrast, AI agents interpret data, learn patterns, and make decisions without hand-coded rules for every scenario. They handle variability and ambiguity much better than static automation.
AI agents vs human-operated processes
Human-operated processes rely on people to interpret data, make judgments, and perform tasks which can be slow, inconsistent, and resource-intensive.
AI agents work continuously, don’t tire, and can act instantly on data across systems accelerating scale and responsiveness in ways humans alone cannot match.
Where traditional workflows break down at scale
- Volume overload: Manual processes collapse with massive data or requests.
- Inconsistency: Human decisions vary by time, mood, and experience.
- Slow feedback loops: Traditional systems can’t adapt in real time.
AI agents overcome these by automating decisions and adjusting strategies based on outcomes.
How A Business Owner Can Use Them in Their Business
AI agents are tools and business owners must choose where they add value.
Identifying tasks suitable for AI agents
Suitable tasks typically have:
- Repetitive decision steps
- Data-driven outputs
- Clear goals (e.g., qualify a lead, route a ticket, summarize reports)
These are prime candidates for AI agents because agents can observe, decide, and act repeatedly without fatigue.
Internal vs customer-facing AI agents
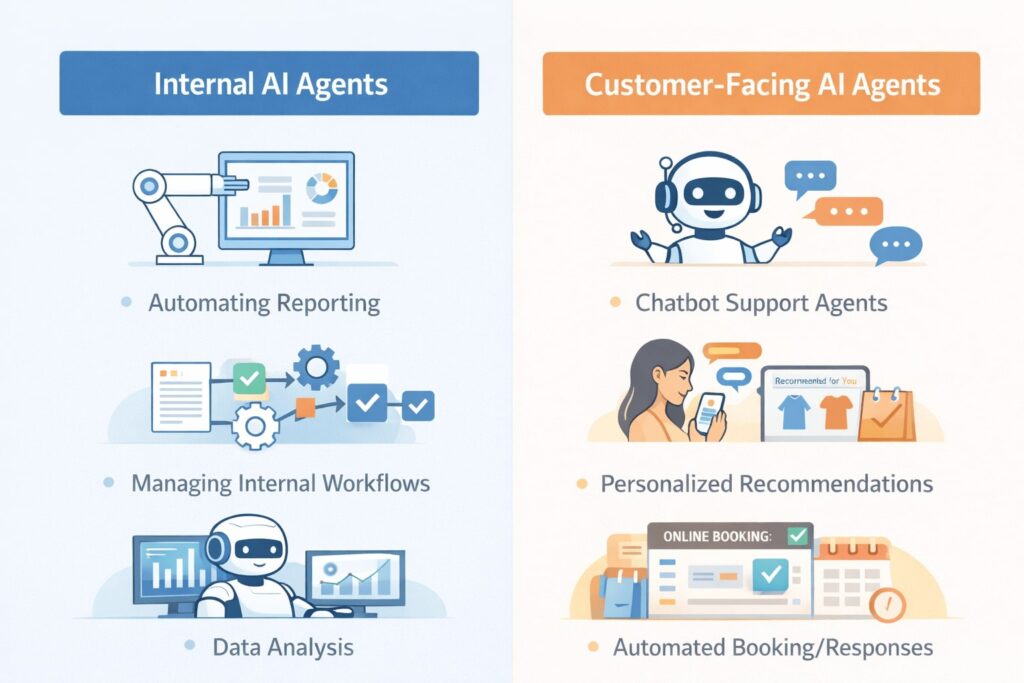
Internal AI agents
Used for operations, analytics, and decision support, such as:
- Automating reporting
- Managing internal workflows
- Data analysis
Customer-facing AI agents
Interact directly with customers, such as:
- Chatbot support agents
- Personalized product recommendations
- Automated booking/responses
Starting small with a single AI agent use case
Best practice — begin with one focused pilot before scaling. Choose a high-impact area like:
- Lead qualification
- Customer support triage
- Simple data reporting
This helps establish proof of value and allows iterative improvement before organization-wide rollout.
Real-world business use cases
AI agents for sales and lead qualification
AI agents can automatically evaluate inbound inquiries, score leads based on engagement data, and even initiate follow-up outreach accelerating lead conversion without human delay.
AI agents for customer support and operations
From 24/7 chat agents that handle FAQs to workflow agents routing operational exceptions, they reduce human workload while increasing responsiveness.
AI agents for marketing and data-driven decisions
AI agents can analyze campaign performance, suggest segmentation, and even generate optimized recommendations for future content — enabling faster strategic marketing adjustments.
When a business should and should not use AI agents
Signs your business is ready for AI agents
- Repetitive tasks burden employees
- Decision tasks can be standardized
- High data volume exceeds manual capacity
- Customer experience demands instant responses
Scenarios where AI agents add little value
- Highly unstructured creative work
- Tasks requiring nuanced human empathy
- Rare, one-off decisions with no predictable pattern
Risks and limitations business owners should consider
- Bias and errors — Agents may reinforce biased training data if unchecked.
- Security & privacy — Agents often access sensitive business data.
- Over-automation risk — Overdependence without proper oversight can miss strategic nuance.
Businesses must build governance and monitoring around their AI agents.
What’s next?
If you’re ready to explore how AI agents could transform your operations, take the next step:
👉 Book a Free Automation Audit — identify high-impact AI agent opportunities tailored to your business goals.







